Comprehensive Overview
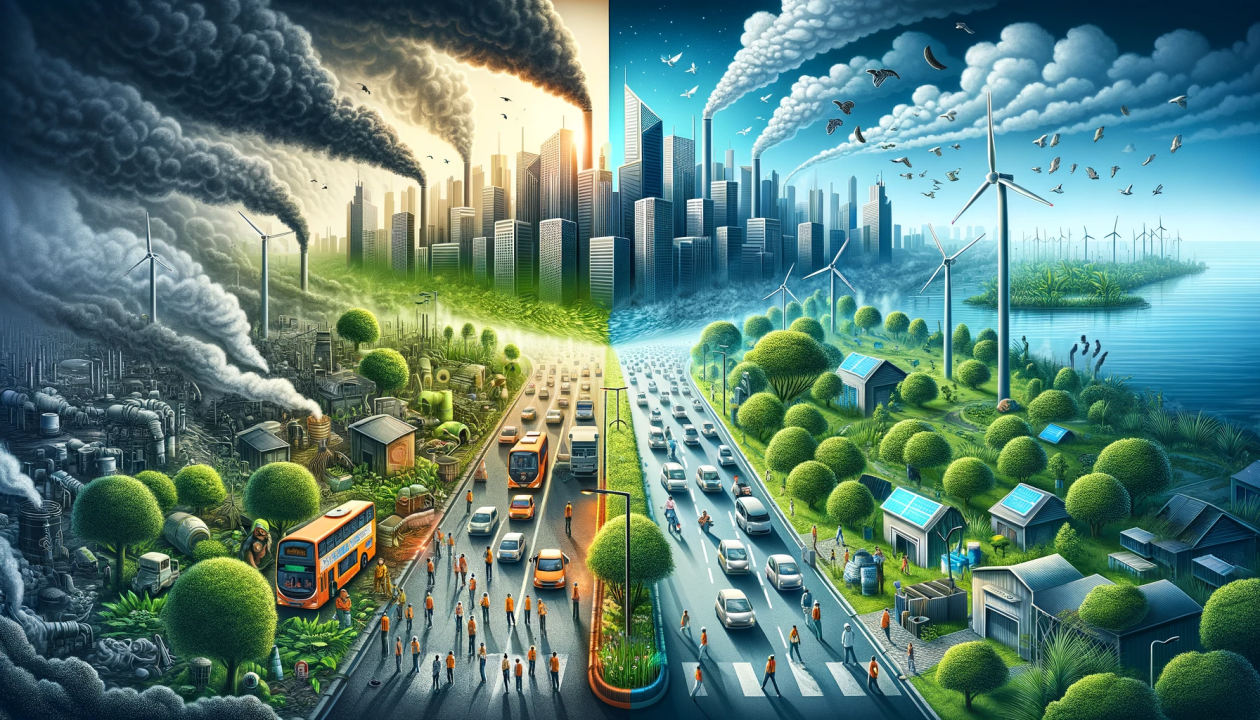
Pollution control is a critical aspect of environmental management that involves implementing measures and technologies to mitigate the adverse effects of pollutants on the environment and public health. It addresses various types of pollution, including air, water, soil, noise, and radioactive contamination, by employing innovative techniques, regulatory frameworks, and community awareness. This comprehensive approach ensures the sustainable coexistence of human activities with nature, safeguarding ecosystems and improving the quality of life.
Smart Sensors: Monitor air and water quality in real-time. Renewable Technologies: Develop cleaner energy sources. Circular Economy: Promote resource efficiency by recycling and reusing materials.
Air Pollution Control
Air pollution is one of the most pressing environmental issues, caused by the release of harmful substances such as carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Effective air pollution control strategies include
Water Pollution Control
Water pollution arises from industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and domestic waste, leading to contamination of rivers, lakes, and oceans. Key water pollution control measures include
Noise Pollution Control
Noise pollution, often overlooked, affects mental and physical well-being. Control measures include
- Urban Planning: Creating noise buffers such as green spaces and sound barriers.
- Vehicle Regulations: Setting permissible noise levels for vehicles and promoting electric vehicles.
- Industrial Controls: Installing noise-dampening equipment in factories.
- Public Awareness: Encouraging community action to reduce unnecessary noise.
Radioactive Pollution Control
Radioactive pollution poses severe risks to human health and the environment. Strategies for control include
Technology in Pollution Control
Advancements in technology play a pivotal role in pollution control. Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and satellite monitoring provide real-time data and predictive analytics to combat pollution effectively. For instance
Role of Policy and Regulation
Governments worldwide enforce environmental laws and policies to control pollution. International agreements like the Paris Accord and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) guide nations toward collective environmental responsibility. Local governments implement zoning laws, pollution taxes, and subsidies for clean energy to support these initiatives.
Public Participation and Awareness
Public involvement is essential for effective pollution control. Awareness campaigns educate individuals about the impacts of pollution and how they can contribute to mitigation efforts. Activities such as tree planting drives, clean-up events, and recycling programs engage communities in sustainable practices.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite advancements, pollution control faces challenges such as inadequate funding, lack of public awareness, and resistance from industries. Future efforts must focus on integrating technology, enhancing international cooperation, and fostering a culture of environmental responsibility.

 Home
Home



 Environmental
Environmental Testimonials
Testimonials






